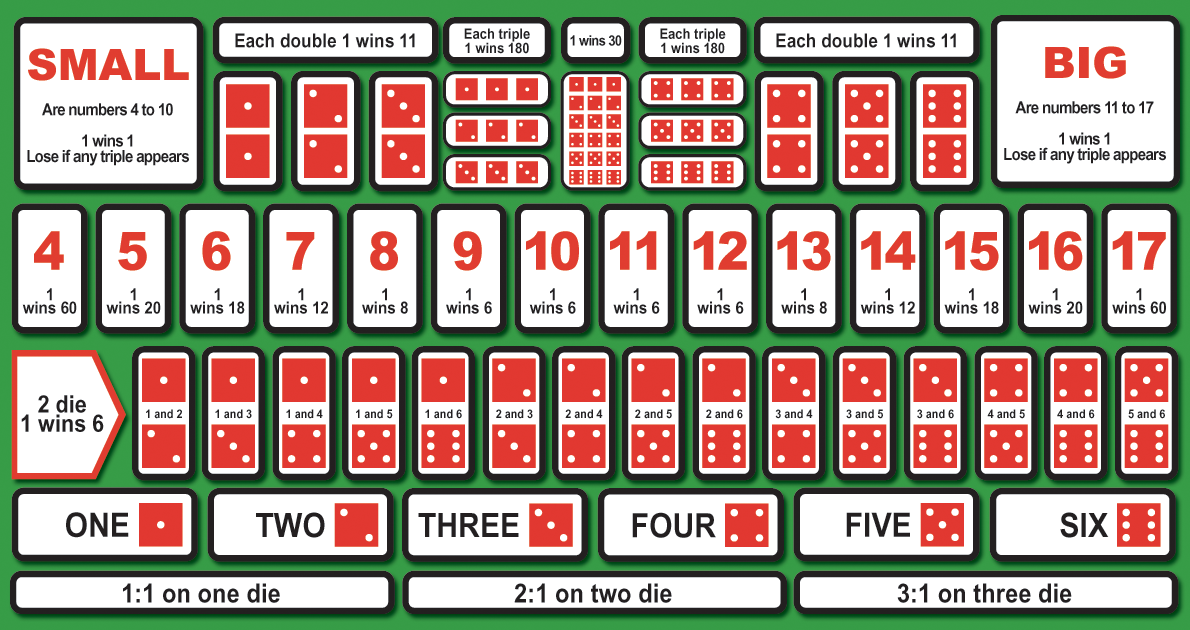
Craps Python 3
In this chapter we will develop two programs involving loops that are slightly more involved than the simple examples from the last chapter.
1.1. Example: the game of craps¶
For the first example, we’ll write a program that allows a user to play the game of “craps”. It is played by rolling a pair of dice. Normally, the player (and spectators) bet on the outcome. We assume that a player starts with a fixed amount of money, called the “bankroll.”

- The game of Pig is a multiplayer game played with a single six-sided die. The object of the game is to reach 100 points or more. Play is taken in turns. On each person's turn that person has the option of eit.
- Compatible with Python 3.8 BlackJack Game in Python 3.8 By Ahmed Q. Sign up for free to join this conversation on GitHub. Already have an account?
- Craps in Python. GitHub Gist: instantly share code, notes, and snippets.
- An introduction to writing a Craps program in Python based on pseudocode. An introduction to writing a Craps program in Python based on pseudocode.
Craps is played like this. Each round of the game has two “phases”:
In the first phase, you roll the dice once. If the result is 7 or 11, you win immediately and the round ends. If the result is 2, 3, or 12, you lose immediately, and the round ends. In all other cases the number you roll (which has to be a 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, or 10) is called the “point”, and you go on to the second phase.
Time again for a game script. How it works This is a classic “roll the dice” program. We will be using the random module for this,since we want to randomize the numberswe get from the dice. We set two variables (min and max), lowest and highest number of the dice. We then use a.
In the second phase you keep rolling the dice until you roll a 7 or you roll the value of the “point” from the previous phase. If you roll a 7 first, you lose, and if you roll the point first, you win.
The payoff for the bets is always one-to-one: if you bet $10 and win, the bank gives you $10.
We can simulate rolling the dice using the randint function. To make it interactive, we’ll use an input statement to pause until the player presses the “Enter” key. Then we just generate two random values 1 through 6 and add them together.
We’ll start by writing a function to play a single round. We can assume that the amount of the bet is a parameter to the function, and the return value of the function is the amount won, where a negative number means a loss. The logic for the first phase just needs a conditional statement.
For the second phase, the player has to keep rolling the dice until she rolls a 7 or rolls the point. There is no way to predict how long that might take, right? So we’ll need a while-loop.
Step 1: What is the repeated action?
Step 2: How do we start out?
Step 3: How do we know whether to keep doing it?
When the loop finishes, we know that the value of ?roll? is either equal to 7 or equal to the point. We just have to check which one, in order to determine whether the player won or lost.
Here is the complete function:
To make this into a complete application, we need a user interface. The interface should allow the user to play again or quit, it should allow her to choose how much to bet, and should keep track of how much she’s won. This could be similar to the user interface for the number-guessing game in the last chapter. This part is left as an exercise.
1.2. Example: a loan table¶
In this section, the problem we are solving is based on the following scenario. Suppose you buy a car and you are making monthly payments. Two years later, you discover you need to trade it in for a minivan. How much do you still owe on your car?
The answer to a question like this is found by creating something called an “amortization table” for the loan. This is just a table that shows for each payment, how much went to pay interest, how much went towards paying off what you owe, called the principal, and how much you still owe, called the balance.
As always, we’ll start with a small concrete example. Suppose you borrow $100 at an interest rate of 10% per month, and you make monthly payments of $30. A month goes by, and you make your first payment. After that, how much do you owe?
The interest you owed for the month is 10% of 100 dollars, or 10 dollars.
The amount paid on your loan is 30 - 10 , or 20 dollars.
The balance you owe is now 100 - 20, or 80 dollars.
We can summarize all this by writing one line in a table:
Then, you make your second payment.
Next month you make another payment.
The process is similar for the next payment.
But now something different happens.
The interest you owe is 10% of 7.18, or 72 cents.The total amount you still owe is the 7.18 balance + 72 cents interest, which is a total of 7.90.Another 30 dollar payment would be too much! So you make a final payment of 7.90, and then the balance is zero
We’ll put the code into a function. The function needs three pieces of information: the amount of the loan, the payment amount, and the interest rate, so our function will have three parameters.
defprint_loan_table(amount,payment,annual_rate):
Let?s analyze what we have done and try to write the code.

Step 1: what is the repeated action?
Look at the calculations we did over and over again:
Introducing some appropriate variable names, we can write these steps by following what we did for the examples. For instance, in the first step, we had a balance of 100 dollars. We found the interest by multiplying the balance by the monthly rate of 10 percent. We found the amount paid on the principal by subracting the interest from the payment amount. We found the new balance by subtracting the principal from the balance.
To print a line of the table, we?ll use a format string with 12 spaces per column. Using a format specifier of ?percent 12 point 2 f? will round everything to two decimal places.
print('%12.2f%12.2f%12.2f'%(interest,principal,balance))That takes care of the loop body.
Step 2: how do we start out?
Initially the balance is the original amount borrowed. The monthly rate is the annual rate, divided by 12. At this point we have this much written. The statements representing the “repeated action” become the loop body.
Step 3: How do we know whether to keep doing it?
Looking back at our example, we knew it was the end when the amount we owed was only 7.90, which was less than the payment. So the loop should look something like this:
How did we know the amount owed? It was the balance, plus the interest for the month, that is:
balance+balance*monthly_rate
So we could write the condition as
Python 3 Craps
while(balance+balance*monthly_rate)<=payment:
That takes care of the loop, but we’re not quite done. We still have to write the very last line of the table showing the final payment.
The complete function is shown below.
Craps Python 3d
Craps -The Intimidating Table Game?
Who hasn’t walked past a craps table the first time feeling intimidation and excitement at the same time? Everybody that’s who!
Nevertheless, it doesn’t stop the curious from learning the game as quickly as possible. Novice player or not - it is for the real gambler, wanting real money action.
Learn the ins and outs and that daunting sentiment quickly disappears. It’s not like the Hollywood portrayal of high-roller James Bond types. A dress code of men in white tuxes sipping on martinis and lovely ladies blowing on their dice isn’t reality.
Come as you are…shorts, sandals, beer in hand and a stack of chips
…and the best part is, it applies to online craps or land-based casinos!
Is Craps a Hard Game to Learn?
It might seem overwhelming and confusing at first. But let’s be honest that goes for anything when not well studied. With a bit of research, you’ll beat the house and be bumping elbows with the best of players. After all, it could be you as the next craps champion
Basic 'Must Knows'
Does the roll of the dice have any impact of the game? That is one controversial question with many players having their own theories. Watch each die long enough and decide for yourself!
Python 3 Craps Game
Practice playing craps with my new and improved craps game.
Read MoreRead LessRules
- 3-4-5X odds are allowed.
- To simplify the game, instead of offering both place and buy bets, I offer just one for each number. Each number pays the better odds between place and buy bets. I refer to these as 'buy bets.' They pay 7-6 on the 6 & 8, 7-5 on the 5 & 9, and 39-20 on the 4 & 10.
- Lay bets pay true odds, but player must prepay a 5% commission, based on the possible win. This works out to odds of 19-25 on the 6 & 8, 19-31 on the 5 & 9, and 19-41 on the 4 & 10.
- If the player selects 'keep bets working,' then all bets will be on for come out rolls. Otherwise, buy, hard ways, and odds on come bets will be turned off.
- If the player selects 'leave winnings bets up,' then only wins will be returned and the original wager will be re-bet. However, winning come and don't come bets are always returned. Winnings odds bets on come bets will remain up if there is a new come bet to associate them with. If the new come bet is less than the winning one, the amount of odds on the table will be the same multiple bet on the odds of the winning bet and the rest returned to the player.
- Bets may be taken down by shift-clicking.
- Put bets and taking down don't pass and don't come bets, that are already on a number, are not allowed.
To slow down the payment stage of the game, hold down the shift and control keys when you click 'roll'.
For fans of my buggy old version one, I still have it. However, I highly recommend playing this current version instead.
Best Real Money Online Craps Bonuses
Online Craps Bonuses
There are a bunch of craps bonuses out there, but not all of them are created equally. With our years of combined experience dealing with casinos, we have sought out to find the best craps bonuses, and have combined them together into the following table.
| Rank | Casino Name | Bonus | % | Wager | Cash | Code | Casino Name | Bonus info | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Win A Day Casino | 🧙 | $68 | - | FREE68LCBN | ||||
| Win A Day Casino | Bonus | 🧙$68 | |||||||
| % | |||||||||
| Wager | - | ||||||||
| Code | FREE68LCBN | ||||||||
| 2 | 21 Casino | 🧙 | £50 | - | |||||
| 21 Casino | Bonus | 🧙£50 | |||||||
| % | |||||||||
| Wager | - | ||||||||
| Code | |||||||||
| 3 | Drake Casino | $2000 | 300% | 450xB | |||||
| Drake Casino | Bonus | $2000 | |||||||
| % | 300% | ||||||||
| Wager | 450xB | ||||||||
| Code | |||||||||
| 4 | BetChain | €200 | 100% | 1000xB&D | |||||
| BetChain | Bonus | €200 | |||||||
| % | 100% | ||||||||
| Wager | 1000xB&D | ||||||||
| Code | |||||||||
| 5 | Zet Casino | €500 | 100% | 300xB&D | |||||
| Zet Casino | Bonus | €500 | |||||||
| % | 100% | ||||||||
| Wager | 300xB&D | ||||||||
| Code | |||||||||